Arthroscopy
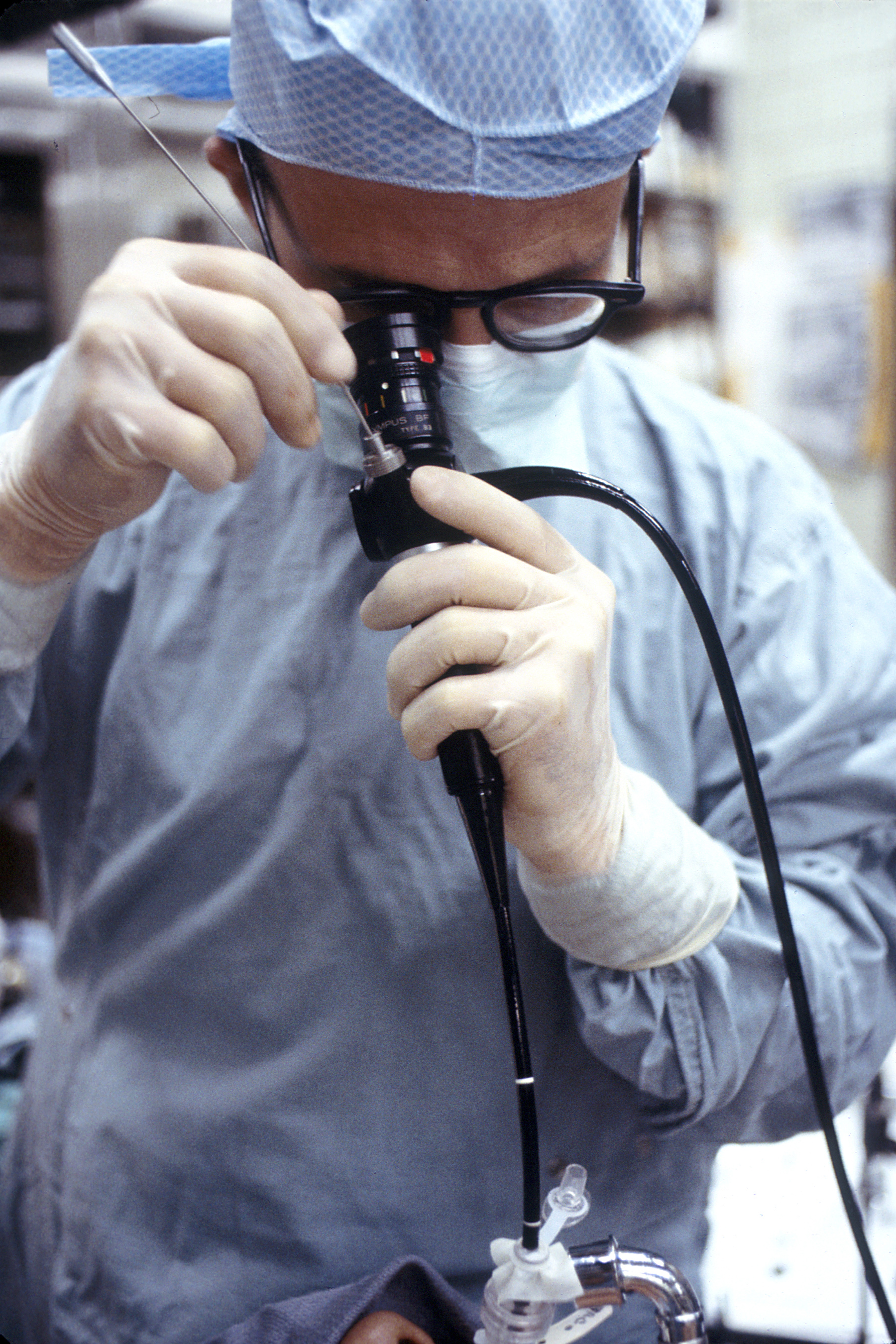
Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive technique that uses optics under 4 mm connected to a camera to see inside the joint.
Diagnose and treat the problems identified in the same procedure. Although done in an operating, do not need to stay overnight in the hospital. Also, reduces recovery time compared to traditional surgery techniques.
Arthroscopy is used to treat various joint problems, among themselves:
Knee
- Meniscus lesions, meniscus transplant
- ACL Injury
- Injury of the posterior cruciate ligament
- Articular cartilage lesions
- Removal of loose bodies (fragments of the cartilage TEJIDOS)
Shoulder
- Rotator cuff injuries
- Shoulder Instability
- Biceps Tendon Injury
- Osteoartritis
- Removal of loose bodies
Ankle
- Impingement syndrome injury to the lateral ligament
- Articular cartilage lesions
- Removal of loose bodies
Wrist
- Articular cartilage lesions
- Lesions of the triangular fibrocartilage
- Diagnosis and treatment of carpal instabilities
- Stiffness after fractures
- Removal of loose bodies
- Ganglion cyst of the synovial
- Elbow
Sequelae of fractures (elbow stiffness)
- Artrólisis, (an operation in which some elements of a joint are cut to restore mobility and adhesions that cause rigidities are released)
- Removal of loose bodies
- Epicondilitis
- Ligament injury diagnosis
- Hand
- Joint trapeciometacarpiana.(rizarthrosis)
Column
- Endoscopy for resection of osteophytes. Osteophytes are some bony growths appear at the ends of the bones sometimes press on nerves and the column and, They can be very painful.
- Exéresis of discal hernia
Hip
- Loose bodies
- Syndrome pinzamiento shock fémoro- acetabular
- Cleaning infections
- Painful diagnostic prosthesis
- Ilio tendon release- psoas
- Pyramidal Syndrome
- Trocanteritis
- Snapping hip
- Advantages of arthroscopy
Advantages of arthroscopy
- The incisions are minimal and do not need to fully open the joint as in traditional surgery.
- Reduces recovery time.
- You can increase the chances of success to be less trauma to the connective tissues (separating those, support or join other tissues or organs).
- Although arthroscopy involves hospitalization, normally no need to stay overnight in the hospital.
What is
The orthopedic surgeon makes a tiny incision (5 mm) in the patient's skin where a small camera, a lighting system and the instrumental precision with which, necessary, will correct the problems detected. Through the camera, The surgeon displays at all times, clearly and in great detail, the inside of the joint on a TV screen.
Arthroscopy is indicated to make the diagnosis when there are joint problems, inflammation as the stiffness, and initial diagnostic tests through the image are not able to find the cause.
Surgery that is required and the recovery time will depend on the complexity of the problem. Sometimes the surgeon, you may discover during arthroscopy that the injury or illness can not be treated adequately with arthroscopy alone and will need to open the joint by traditional surgery. The surgeon can then perform this operation, or plan it for another day.
What is it
This procedure can be examined almost all joints, but most of arthroscopic knee and shoulder are. Arthroscopic knee surgery is being performed for longer.
Originally it was used to remove bone fragments, cartilage or a torn meniscus inside the knee.
Nowadays, complex arthroscopic surgical procedures are performed, as ligament reconstruction (as the ligaments of the knee), certain fractures (as the tibia), repair torn tendons (around the shoulder), reconstruct the shoulder and, and general, identify problems that otherwise could not be known before practicing arthroscopy.
Arthroscopy is also used to treat the ankle, Doll, elbow and hip.
See Table arthroscopy some problems treated with arthroscopy
To arthroscopy surgery can basically use three types of anesthesia:
- Local anesthesia. Which numbs the area of the joint. Administered with relaxant drugs. The patient does not lose consciousness at all, but remains awake, in a relaxed state, without anxiety, painlessly and drowsiness.
- Anestesia regional. The patient will not feel anything from the waist down, but awake.
- General anesthesia. The patient will be completely asleep. In arthroscopic shoulder or when regional anesthesia is contraindicated, General anesthesia is used.
The anesthetist will decide which type of anesthesia is most suitable in each case.
Before arthroscopy
Before undergoing arthroscopy, the orthopedic surgeon will perform a thorough physical examination, to assess your health and identify any problems that may interfere with surgery.
The surgeon may ask preoperative examinations, as the analysis of an electrocardiogram bled.
- Talk to your doctor, never hesitate to ask what you do not understand or convey their doubts and fears.
- Do not eat anything after midnight the day before undergoing arthroscopy, not drink alcohol or smoke.
- Tell your doctor about any medications or supplements you are taking.
- Complications in arthroscopy are rare (less than 1% of total). The most common are: infection incision, weep (Blood clots in the vein) in the affected limb, hinchazón o hemorragia.
After arthroscopy
Small incisions takes a few days to heal, although the dressing operation can be removed the day after arthroscopy. Normally the joint takes several weeks to recover fully. You can return to everyday activity within a few days and sporting activities, when the doctor advises. Arthroscopy is unique to each person, so that the recovery time will depend on the diagnosis and the nature of the ailment.
The doctor will prescribe pain medication to help relieve discomfort you may feel after arthroscopy. You can also recommend medications, like aspirin, to reduce the risk of blood clots forming.
In order to speed recovery and to protect the joint function, the doctor will suggest a rehabilitation program.
- Usually one or two hours will remain under observation and then he would return home.
- You may feel some discomfort: mild pain or light bleeding in areas of the incisions.
- In some cases it may be necessary to place some form of immobilization.
- Follow your doctor's instructions to facilitate the recovery of joint mobility and prevent complications.
- If the pain is severe, no inflammation, Pour fiebre, contact your doctor immediately.